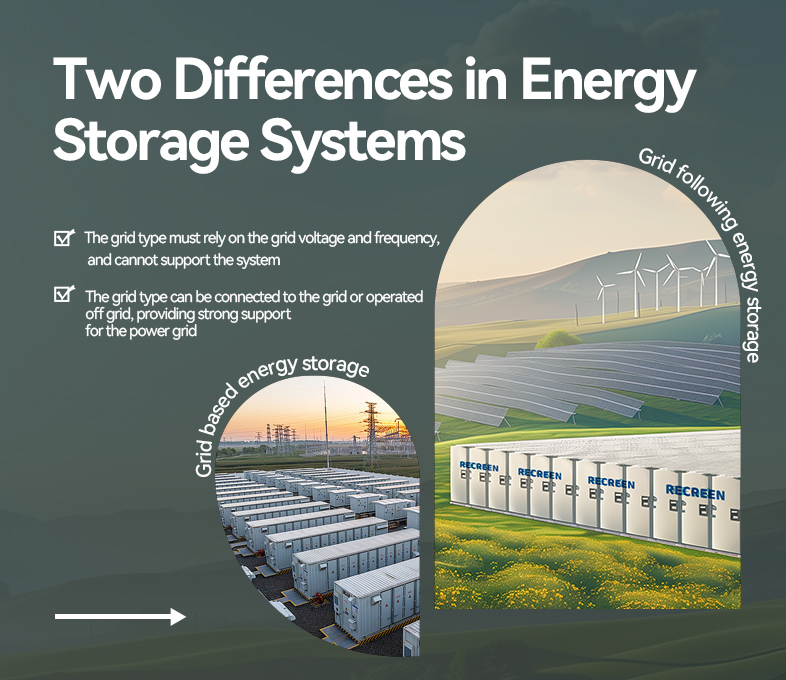
Introduction
Amid the global energy transition, energy storage has emerged as a crucial technology, drawing attention from businesses and policymakers alike. Among the various storage solutions, Commercial & Industrial (C&I) Energy Storage and Large-Scale Energy Storage are two commonly applied models. This article provides a comprehensive comparison between the two, helping readers better understand their unique characteristics and application scenarios.
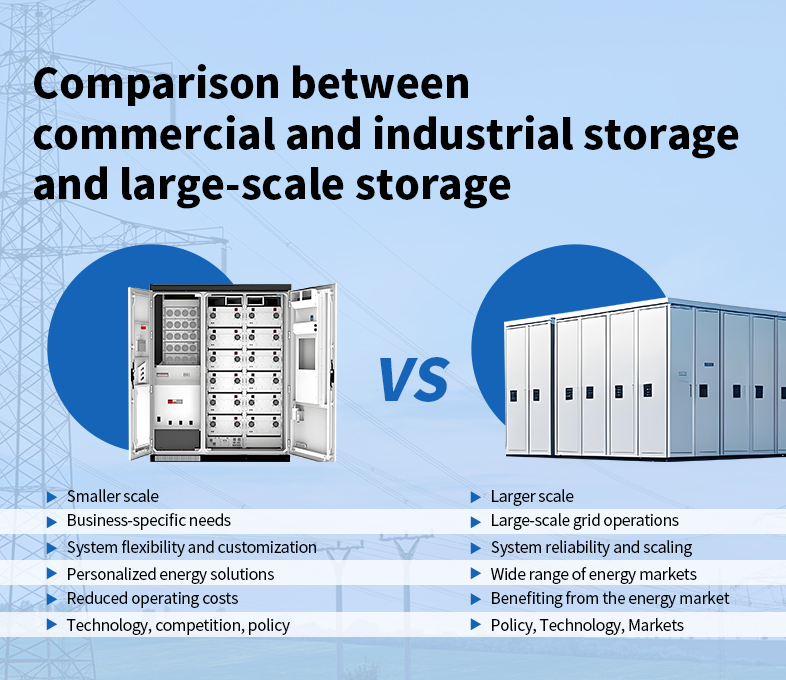
1. Scale & Capacity
The primary difference between C&I storage and large-scale storage lies in their target users and capacity requirements.
C&I storage caters to commercial and industrial users, with a smaller scale, typically ranging from a few kilowatts (kW) to several megawatts (MW).
Large-scale storage serves broader energy markets and the grid, with higher capacities, often in the tens or even hundreds of MWs.
2. Application Scenarios
C&I Storage Applications:


Large-Scale Storage Applications:


3. Technology Pathways
Both C&I and large-scale storage predominantly rely on lithium-ion batteries, lead-acid batteries, and other electrochemical storage technologies. However, there are distinct differences:
C&I storage prioritizes flexibility and customization to meet various business needs.
Large-scale storage emphasizes reliability and scalability to support grid-level operations.
4. Business Models
C&I storage and large-scale storage also differ in their business models:
C&I storage models include direct purchase, leasing, and partnerships with energy service providers, focusing on tailored energy solutions for businesses.
Large-scale storage often engages in power market trading, demand response, and ancillary grid services, leveraging broader energy market opportunities.
5. Revenue Models







6. Risks & Challenges
Both storage types face distinct risks and challenges:
C&I storage is susceptible to technological updates, market competition, and policy changes, requiring businesses to choose appropriate technologies and strategies.
Large-scale storage faces complex system integration, grid security concerns, and market access challenges, necessitating multi-faceted considerations across policy, technology, and market dynamics.
7. Future Outlook
With the continued acceleration of global energy transition, both C&I and large-scale storage will experience tremendous growth opportunities. Advancements in technology, market expansion, policy support, and cross-sector collaborations will drive further innovation. To achieve a green, low-carbon, and sustainable energy future, stakeholders must work together to ensure the healthy development of the energy storage industry.
Conclusion
Despite differences in scale, applications, technology, and business models, both C&I and large-scale storage play a vital role in energy transition and sustainable development. Understanding and investing in both storage models will be essential in shaping the future energy landscape.