In the context of the rapidly developing renewable energy sector, the energy storage inverter plays a crucial role in connecting renewable energy systems to the grid or load. In this regard, off-grid energy storage inverters and hybrid energy storage inverters have gained significant attention due to their unique working principles and application scenarios. This article provides a brief introduction to the basic principles of these two inverters and emphasizes their main differences.
01 Functional Features
Off-grid Energy Storage:
- The main function of an off-grid energy storage inverter is to convert DC power generated by solar panels into AC power for load use.
- It is usually equipped with energy storage batteries to store excess energy and release it when needed.
- It operates independently and is suitable for remote areas or areas without access to the grid.
Hybrid Energy Storage:
- It combines both off-grid and on-grid functions, providing bidirectional flow of electricity. It can convert DC power from solar panels into AC power for load use as well as being connected to the grid.
- When the grid is available, it can supplement the insufficient solar energy generation with electricity from the grid. When the grid is unavailable, it can operate in off-grid mode to provide electricity to the load.
- It has efficient inverting capabilities and intelligent charging functions, which can adjust charging parameters automatically according to the battery status, thereby extending the battery life.
02 Application Scenarios
Off-grid Energy Storage:
- It is mainly used in remote mountainous areas, deserts, islands, and other areas without access to the grid or where the grid is unstable.
- It is suitable for households, small commercial projects, or places that require independent power supply.
Hybrid Energy Storage:
- It is suitable for places with access to the grid and where people want to reduce their electricity costs or achieve energy self-sufficiency with solar power generation.
- It is suitable for households, businesses, public facilities, and other places, especially in areas with unstable power supply or where people want to improve energy efficiency.
03 Differences Between the Two
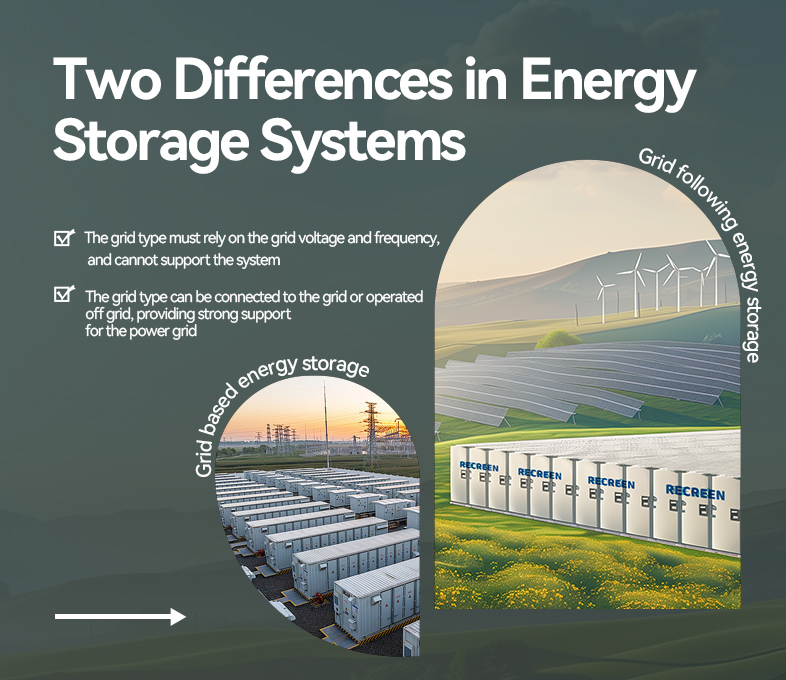
Working principle:
Off-grid Energy Storage: When the grid has excess power or solar power generation, the energy is stored in the battery. When electricity is required, the DC power is converted into AC power from the battery to the load.
Hybrid Energy Storage: It can switch automatically between on-grid and off-grid modes based on the grid status. In on-grid mode, the excess renewable energy is fed into the grid. In off-grid mode, the battery is used to power the load.
Application Range:
Off-grid Energy Storage: It is suitable for remote areas, islands, nomadic areas, and other areas without access to the grid or areas with unstable power supply.
Hybrid Energy Storage: It is suitable for large-scale renewable energy generation stations, micro-grids, and other places that require both on-grid and off-grid functions.
Protection Level:
Off-grid Energy Storage: It is generally installed indoors with lower protection class requirements, usually IP20.
Hybrid Energy Storage: Due to its outdoor and rooftop installation scenarios, it has higher protection class requirements, usually IP65 and above.
Complexity:
Off-grid Energy Storage: The system is relatively simple, focusing mainly on self-sufficiency.
Hybrid Energy Storage: The system is more complex, with more functions and more complex control strategies, which can better adapt to various complex power environments.
Price and Lifespan:
Due to the higher complexity of hybrid energy storage inverters, their costs are usually higher than that of off-grid energy storage inverters. Correspondingly, hybrid energy storage inverters have higher energy utilization efficiency and system stability.
In summary, off-grid energy storage inverters and hybrid energy storage inverters each have their advantages and suitable application scenarios. Users should consider various factors such as actual needs, cost budget, and application scenarios when choosing.