Residential energy storage systems involve complex architectures and various devices such as batteries and inverters. Currently, products in the industry are independent of each other, which can lead to various issues in practical use. The main challenges include complex system installation, difficult operation and maintenance, inefficient utilization of energy storage batteries, and low battery protection levels.
1. System Integration: Complex Installation Residential energy storage is a complex system that combines multiple energy sources and targets ordinary households. Most users expect it to be used like “home appliances,” which imposes higher requirements on system installation. Currently, complex and time-consuming on-site installation has become a major concern for some users in the residential energy storage market. There are mainly two types of residential energy storage system solutions available: low-voltage energy storage and high-voltage energy storage.
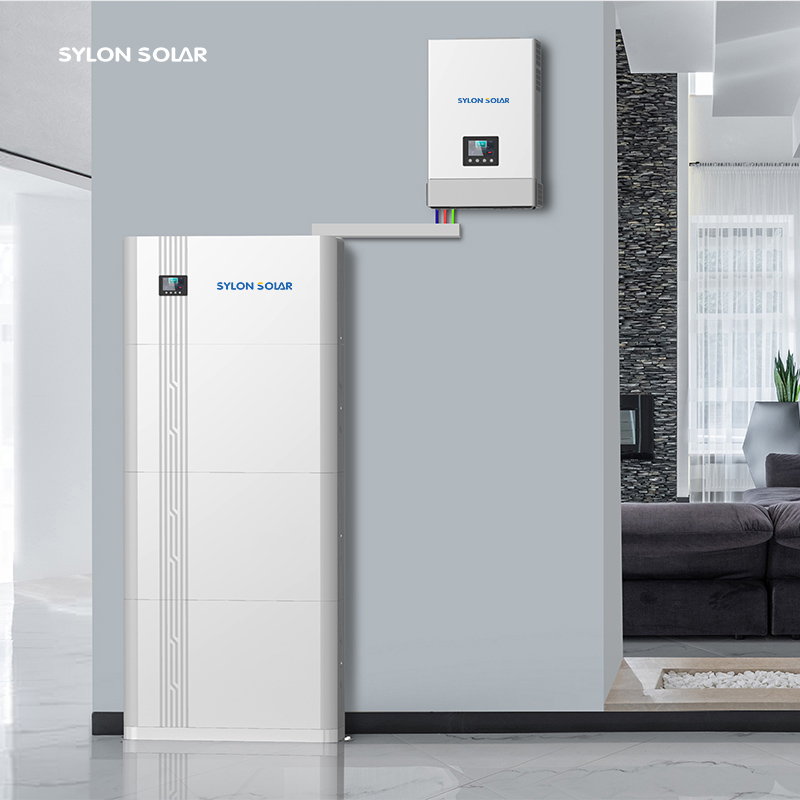
Low-voltage energy storage system (inverter and dispersed batteries): A low-voltage energy storage system refers to an energy storage system with battery voltage ranging from 40V to 60V. It consists of several batteries connected in parallel and connected to the inverter. Through the internal isolation DC-DC of the inverter, it intersects and couples the direct current output from the photovoltaic MPPT at the busbar, and finally converts it into alternating current through the inverter output and connects to the grid. Some inverters also have backup output capabilities.

Main issues with low-voltage energy storage systems:
1.Inverters and batteries are independently dispersed, making the equipment heavy and installation difficult.
2.The connection lines between inverters and batteries cannot be standardized and require on-site processing. As a result, the entire system installation takes a long time and increases costs.
High-voltage energy storage system:
The high-voltage energy storage system for households adopts a two-level architecture, with several battery modules connected in series and outputted through a high-voltage control box. The voltage range is generally from 85V to 600V. The battery cluster output is connected to the inverter, and through the internal DC-DC unit of the inverter, it intersects and couples the direct current output from the photovoltaic MPPT at the busbar, and finally converts it into alternating current through the inverter output and connects to the grid. Some inverters also have backup output capabilities.
Main issues with high-voltage energy storage systems: To avoid directly connecting battery modules from different batches in series, strict batch management needs to be implemented in production, shipping, warehousing, and installation. This requires a large investment of manpower and resources, and the process can be tedious and complex, causing difficulties in stock preparation for customers. In addition, the self-discharge and capacity degradation of batteries can widen the differences between modules, and general systems require manual charging if the differences are significant, which is time-consuming and labor-intensive.
Product Operation and Maintenance: High Technical and Cost Thresholds To ensure the reliable and safe operation of residential energy storage systems, effective operation and maintenance are essential measures.
However, due to the relatively complex architecture of high-voltage energy storage systems for households, high professional requirements are placed on maintenance personnel. In practical use, there are often difficulties and time-consuming issues in maintenance, mainly due to the following reasons:
1.Regular maintenance requires SOC calibration, capacity calibration, or main circuit inspections of battery clusters.
2.When battery modules have abnormalities, conventional lithium batteries do not have automatic balancing functions, so maintenance personnel need to manually charge the batteries on-site, which cannot quickly respond to customer demands.
3.Mixed Use of New and Old Batteries: Accelerated Aging and Capacity Mismatch In the case of mixing old and new lithium batteries in low-voltage energy storage systems, the significant difference in internal resistance can cause circulation, leading to increased battery temperature and accelerated aging of new batteries. For high-voltage energy storage systems, the mixed use of old and new battery modules in series can lead to severe capacity mismatch due to the barrel effect. New battery modules can only be used based on the capacity of the old battery modules. The battery cluster will experience significant capacity loss. For example, if the usable capacity of a new module is 100Ah and the usable capacity of an old module is 90Ah, mixing them together would result in a battery cluster with a usable capacity of only 90Ah. Therefore, it is generally not recommended to directly connect or parallel old and new lithium batteries.