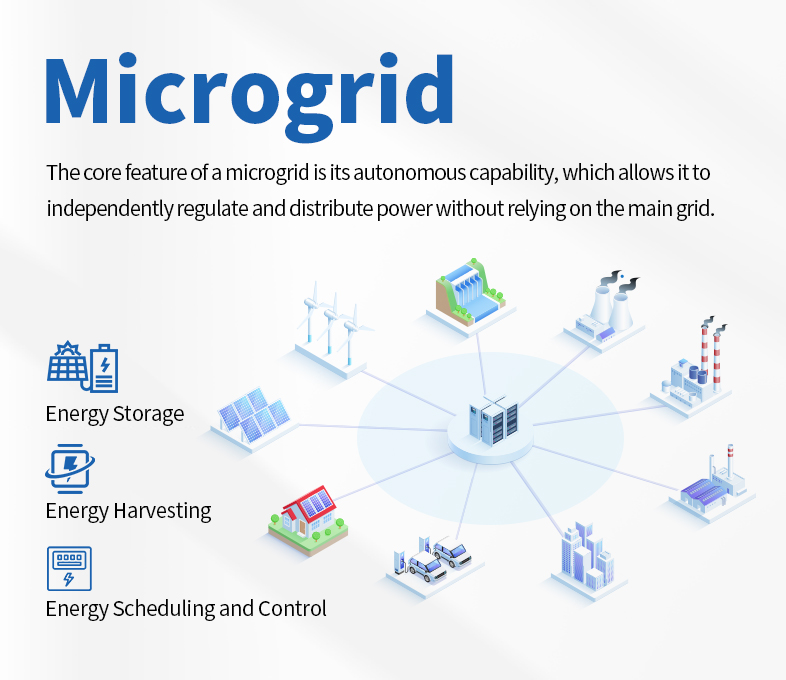
Q What is a Microgrid?
A A microgrid is a high-efficiency power system capable of independent control and management, integrating distributed energy sources, energy storage devices, and intelligent control technologies. It can operate flexibly in both on-grid and off-grid modes. The core feature of a microgrid is its autonomous capability, which allows it to independently regulate and distribute power without relying on the main grid. The microgrid integrated with energy storage technology is an important development direction in the current energy sector.
Q How Does a Microgrid Work?
A A microgrid operates through three main steps:
1、Energy Collection: Energy is collected through solar panels or other renewable energy devices and converted into electrical energy. Additionally, electricity can be sourced from the main grid as a backup when needed.
2 Energy Storage: The collected electrical energy is stored in energy storage devices such as batteries, flywheels, or supercapacitors. These storage devices can store energy during periods of low demand and release it during peak demand or grid outages.
3 Energy Scheduling and Control: An Energy Management System (EMS) intelligently controls the charging and discharging processes of the storage devices to meet load demands, smooth out the fluctuations of intermittent energy sources, and optimize the overall operation of the microgrid.
Q What Are the Application Scenarios of Microgrid?
A The integration of microgrids and energy storage systems provides stable, reliable power supply and energy management solutions for various application scenarios. Here are the primary application scenarios for microgrids:
1、Utilization of Renewable Energy
Photovoltaic Power and Storage: In areas with abundant solar resources but limited grid access, such as islands and remote mountainous regions, microgrids with energy storage systems can store excess solar power generated during the day and release it during periods of insufficient sunlight or at night, ensuring continuity and stability of power supply.
Wind Power and Storage: Wind farms also face the challenge of unstable power generation. Energy storage systems can smooth out fluctuations in wind power output, enhancing the grid integration and power quality of wind energy.
2、Critical Infrastructure and Public Services
Data Centers and Storage: Data centers require highly stable power supplies. Energy storage systems can serve as backup power sources to ensure continuous operation during grid failures.
Hospitals and Storage: Hospitals, as critical public service facilities, must have uninterrupted power. Energy storage systems can quickly switch to provide power during grid outages, ensuring the operation of medical equipment and the safety of patients.
5G Base Stations and Storage: 5G base stations have high power consumption and require stable electricity supply. Energy storage systems can act as backup power sources, enhancing the reliability and stability of base station operations.
3、C&I Applications
Industrial Plants and Storage: For industrial facilities with high power consumption and strict stability requirements, microgrids combined with energy storage systems can ensure continuous production and minimize losses due to grid outages.
Commercial Buildings and Storage: Commercial buildings, such as shopping malls and office buildings, experience significant variations in power demand with time and season. Energy storage systems can store energy during off-peak hours and discharge it during peak hours, alleviating grid pressure and reducing electricity costs.
4、Community and Residential Use
Community Microgrids and Storage: Building microgrids equipped with energy storage systems at communities can provide stable and reliable power to residents while promoting the use of renewable energy and reducing energy consumption
Electric Vehicle Charging Stations and Storage: Combining PV systems and energy storage systems with EV charging stations can achieve integrated solar storage and charging. Solar power can be used to charge EVs, and excess energy can be stored for later use. This enhances the self-sufficiency of charging stations and reduces grid load.
5、Specialized Applications
Military Facilities and Storage: Military installations require high stability and security in power supply. Microgrids combined with energy storage systems can ensure continuous power supply during grid outages or external attacks.
Emergency Response and Storage: In emergency situations, such as natural disasters, microgrids combined with energy storage systems can rapidly provide temporary power to affected areas, facilitating effective rescue operations.
Q What Are the Advantages of Microgrid Integrated with Energy Storage Technology?
A 1、Enhanced Energy Efficiency: In a microgrid, the energy storage system can store electricity when solar power generation is abundant and supplement electricity when solar power generation is insufficient, ensuring the stability and reliability of the power supply.
2、Versatility: It supports a range of functions including peak shaving and frequency regulation, energy dispatch and optimization, energy monitoring and management, and integration of renewable energy sources.
3、Improved System Stability: The integration of energy storage in microgrid significantly enhances the stability, reliability, and sustainability of the microgrid, reducing energy waste and fuel consumption.
4、Flexibility and Scalability: Advanced storage technologies allow for flexible upgrades and expansions of the microgrid system based on user requirements, accommodating growth and evolving needs.
5、Disaster Resilience: In special situations such as disasters, microgrids can switch to off-grid mode to provide backup power for the load, ensuring the normal operation of the load.
In summary, microgrids integrated with energy storage technology play a crucial role in various application scenarios, providing strong support for the stability, reliability, and cost-effectiveness of power supply. As technology continues to advance and costs further decrease, the application prospects for microgrids will become even broader.